
Injection Molding vs. Compression Molding: Which Is Better?
⭐ Introduction
When it comes to plastic manufacturing, choosing the right molding process is crucial for achieving the best balance between cost, performance, and production efficiency. Among the many molding techniques, Injection Molding and Compression Molding are two of the most widely used processes—each with its unique strengths.
This article will break down the key differences, advantages, and best-use cases to help you determine which method is better for your product.
1️⃣ What Is Injection Molding?
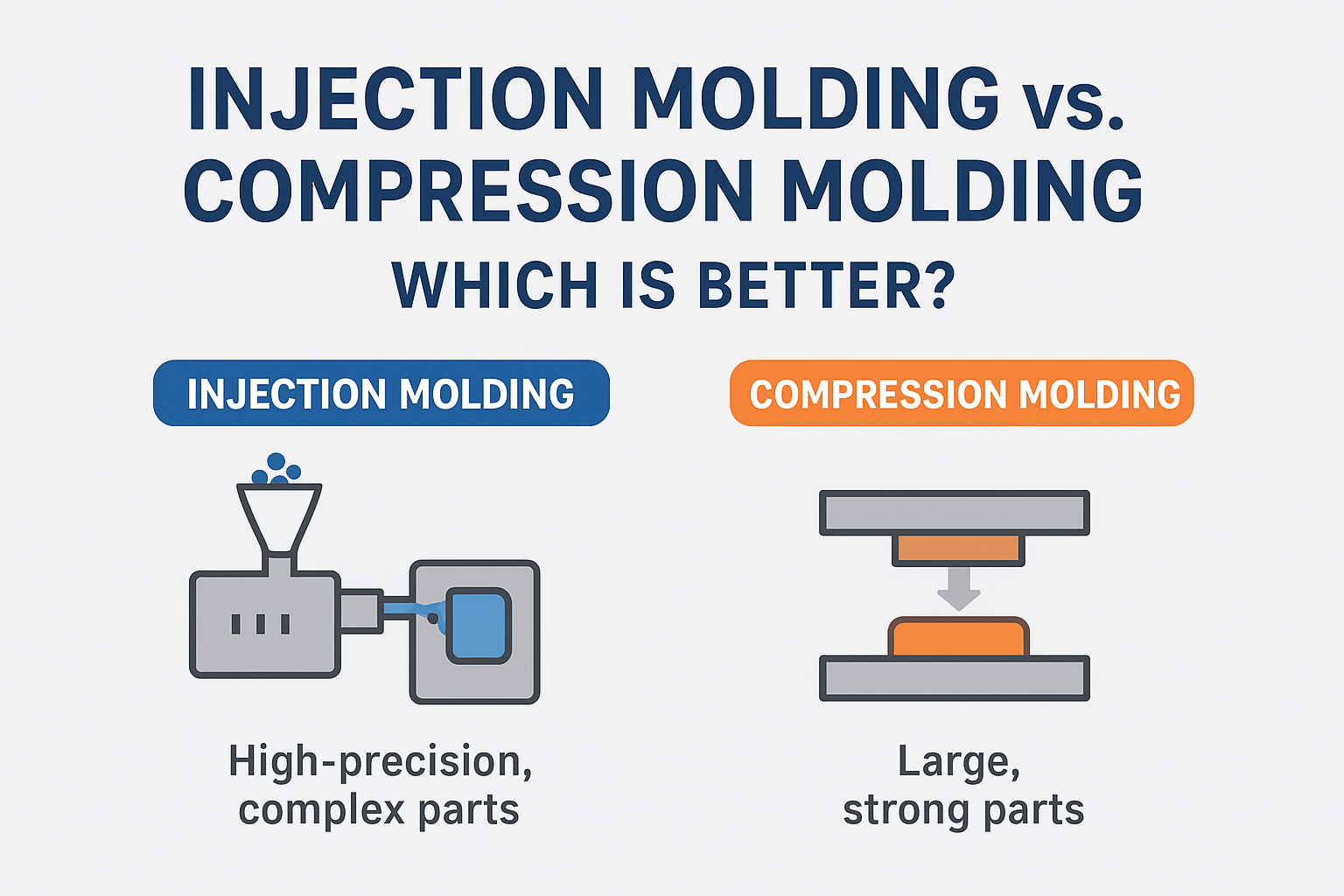
Injection molding is a high-precision manufacturing process where melted plastic is injected into a steel or aluminum mold to create complex, detailed parts.
How It Works:
- Plastic pellets are melted.
- Melted material is injected into the mold cavity.
- It cools and forms the final shape.
- Part is ejected and ready for the next cycle.
Advantages of Injection Molding:
- Excellent repeatability and tight tolerances
- Suitable for high-volume production
- Ideal for complex shapes and thin-walled parts
- Wide material compatibility (ABS, PP, PC, PA, TPE, etc.)
- Fast production cycle once mold is built
Best Applications:
Consumer products, automotive components, electronics housings, medical parts, packaging, tools, small precision items.
2️⃣ What Is Compression Molding?
Compression molding is a process where heated plastic material (often thermosets) is placed in an open mold, compressed with high pressure, and solidified into shape.
How It Works:
- Pre-measured material is placed into the mold.
- Mold closes and pressure compresses the material.
- Heat cures and forms the final part.
- Mold opens and part is removed.
Advantages of Compression Molding:
- More cost-effective tooling than injection molds
- Great for large, strong, durable parts
- Good dimensional stability and strength
- Works well with thermoset materials like epoxy, phenolic, SMC, and fiberglass composites
Best Applications:
Automotive parts, electrical housings, industrial equipment, handles, appliance components, structural parts.
3️⃣ Injection Molding vs Compression Molding: Key Differences
| Feature | Injection Molding | Compression Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Best for | Complex, precision parts | Large, strong structural parts |
| Typical materials | Thermoplastics | Thermosets / composites |
| Tooling cost | Higher | Lower |
| Production volume | Medium to high | Low to medium |
| Cycle time | Fast | Slower |
| Part consistency | Very high | High |
| Design complexity | Excellent | Limited |
4️⃣ Which Is Better?
The answer depends on your project. Here’s a quick guide:
✔ Choose Injection Molding if you need:
- High-volume mass production
- Complex shapes or thin-walled parts
- High precision and fine details
- Thermoplastic materials
✔ Choose Compression Molding if you need: - Large, thick, or high-strength components
- Lower tooling costs
- Thermoset or composite materials
- Good mechanical performance and heat resistance
🏁 Conclusion
Both injection molding and compression molding are highly effective manufacturing processes, but each serves different needs. Injection molding is ideal for high-volume, precision plastic parts, while compression molding is better suited for larger, stronger components using thermoset materials.
If you are unsure which method is right for your project, our engineering team can help you choose the best process based on your material, budget, and application requirements.
📩 Contact us today for technical consultation or a customized quotation!